Reasons Why Your Internet is Slow
It is not difficult to get frustrated when the internet works slowly. Particularly when you need it for urgent work or when you are enjoying streaming or gaming. “Why is my internet so slow?”A slow connection makes it hard to download and upload files and can be exasperating. Figuring out what is wrong with your internet speed is a must to get the problems resolved effectively. Here are several key factors that can lead to a sluggish internet connection.
1. Outdated or Inefficient Router
One of the main reasons behind slow internet speed is an obsolete or inefficient router. Over time, routers break down, and with technology constantly moving forward, the older models may not support faster, new standards. If your router is several years old, it may struggle to handle multiple devices connecting simultaneously. To boost your internet performance drastically, purchasing a new router is smart to think about.
2. Network Congestion
Network saturation occurs when an excessive number of devices are simultaneously connected to a single internet source. It means that it is like a traffic jam; with a lot of cars on the road, everyone’s movement is slowed down. The speed of your internet can be dropped while playing videos or music, downloading files, or playing games online at the same time. Less active devices or an increased internet plan can solve this problem.
3. WiFi Signal Interference
Many interference sources can influence WiFi signals. Overlapping networks in apartment buildings might reduce connection quality. At the same time, walls and furniture might block signals, and home appliances, including microwaves, produce electromagnetic interference. Your network’s performance will be much improved by changing router location and reducing interference sources.
4. Background Applications Consuming Bandwidth
Lots of applications are executed in the background on your devices and take megabytes of bandwidth without your knowledge. This covers automatic updates for the software programs and apps, cloud storage syncing, and even streaming services that may consume data even when you are not using them. Regularly checking which applications are running and closing unnecessary ones can free up more bandwidth for other important tasks.
5. Data Cap Restrictions
A lot of Internet Service Providers (ISPs) impose limits on the data plans that they offer. When you go over this amount—usually due to intense consumption like video streaming or heavy downloading—you may end up getting your rates regulated until your next billing cycle starts. Assessing your data usage and considering the option for an unlimited plan can fix this situation.
6. High Latency
Latency is the time taken by the data to travel from your device to the server and back to your device. High latency can lead to delays in, say, playing games or holding video conferences online. The root causes of high latency are factors like the server being far away, network congestion, and the ISP’s poor routing. To detect the problem, if you experience lag frequently, running a latency test on different servers might do the trick.
7. Outdated Devices
The devices themselves are also a bottleneck for internet speed. The old laptops, smartphones, and tablets may have internet protocols that are outdated or have hardware that is not able to process the data at high speeds. To add to the better overall performance, make sure your devices are always up to date with the latest software and change existing devices if necessary.
8. Poor Wiring or Infrastructure
The infrastructure and connectivity of an internet service provider to your place of residence are crucial in ensuring a stable network. If the cables of the internet service provider are not well maintained or have aged, then you might experience a loss of speeds of meters and a lot of disconnection problems. Your suspicion that the connection is affected by wiring issues can be solved by calling the ISPs for an inspection.
9. ISP Throttling
Some internet providers may deliberately slow down the speeds only for some specific type of traffic or after you have already reached a certain stage by data thereof—a practice known as throttling. Since some of you guys may be unsure whether the slowing down is an outcome in their case, for example, your speeds might go down alone during, for example, times of the day when a lot of other people are in use, then check your connection speed with the VPN software and then without it.
10. Malicious software or viruses
The internet speed can be slowed down because of malware doing operations on your device at the same time or a kind of virus that can be sucking all the bandwidth in your network. To maintain an efficient internet network, you must carry out a security check-up regularly and ensure that the system is not infected with any kind of malware.
Once you know the main offenders behind slow internet speeds, you can properly solve these problems, so improving your digital experience and output.

How to Speed Up Your Internet
Here are a few ways to substantially upgrade your internet speed, regardless of whether you’re watching videos online, gaming, or working remotely, all of which can greatly improve your overall digital experience:
1. Restart Your Modem and Router
- First, unplug the power cable from both devices – the modem and the router.
- 30 seconds, at the least, should be the period to wait.
- Firstly, plug the modem back in, and then do the same with the router.
- Let them reboot for several minutes before you can use them again.
2. Use an Ethernet Cable
For the best and most secure networking, try to connect your computer to your router with an Ethernet cable directly. Wired links are more stable and faster than WiFi, and they do not even have interfering connections.
Tips for Using Ethernet:
- Ensure the cable is of good quality and not excessively long.
- Use a short cable whenever possible to reduce signal loss.
3. Optimize Your Router’s Location
The positioning of your router can greatly determine the speed of your internet at your home.
Best Practices:
- Place the router in the most centralized location in the house.
- We recommend keeping it off the floor and putting it on a shelf or table.
- Please protect it from walls, metal objects, and electronic gears that provoke problems (like microwaves).
4. Update Your Router’s Firmware
To achieve the best results and have a highly secure system, properly you should ensure that you update your router’s firmware frequently.
How to Update:
- Log in to the console of your router using a web browser (usually by typing its IP address).
- Check in the firmware section of the settings menu if there is a newer version available.
- Adhere to the directions that your router manufacturer gives.
5. Clear Your Browser’s Cache
As time goes by, your browser caches different things that can slow it down. You should clear the cache regularly to increase the browser’s speed of downloading the pages.
How to Clear Cache:
- Go to your browser settings.
- It is important to click on “history” or “privacy” settings if you recollect them, or just ” history,” and you will arrive directly there.
- Select the option to clear browsing data, ensuring that cached images and files are checked.
6. Limit Background Applications
Background software consumes more bandwidth than you foresee. When you shut down programs that you do not need, the other programs get the help they need.
Steps on How to Manage Applications:
- To find which applications are consuming a lot of the bandwidth, consult the task manager (Windows) or activity monitor (Mac).
- You should close any non-vital PC applications, particularly the ones that use lots of streaming or downloading content.
7. Change the WiFi Band or Channel
Many routers operate on both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. By selecting the band with fewer users, the speed will be faster.
How to Change Band:
- Open your web browser and go to the router settings window.
- Go to the wireless settings and then pick the band you want (5 GHz can be made faster, but it becomes short-range).
Changing Channels:
- Switching channels on the 2.4 GHz band in densely populated areas can reduce interference from neighbouring networks.
8. Secure Your Network
An unsecured WiFi network allows unauthorized users to connect, thus it can sometimes speed your internet up.
How to Secure:
- Change the default password of your WiFi network.
- Use WPA3 encryption if available.
Regularly review connected devices to ensure no unauthorized users are consuming bandwidth.
9. Upgrade Your Internet Plan
You are always not on the slow internet even after you have the technician troubleshoot it.
What to Consider:
- Review the volume of household data usage (e.g., streaming, gaming) and calculate it accordingly.
- Contact your ISP to inquire about new offerings for faster speeds.
10. Utilize Quality of Service (QoS) Features
Certain routers allow you to schedule different kinds of network traffic through a QoS (Quality of Service) alternative. Furthermore, it lets users reduce any potential latency if they believe it to be essential for their gaming experience.
How to Configure QoS:
- Log into your router’s administration interface through a web browser.
- Navigate to the QoS or Traffic Management settings, which may be located in the advanced settings menu.
- List the services or apps like streaming platforms, online gaming, or video conferences that call for prioritizing.
- Assign higher priority levels to these critical applications while setting lower priority for less essential traffic like file downloads or background updates.
- Save your changes and monitor the impact on your network performance, making adjustments as needed based on your specific requirements and preferences.
Through the application of these technologies, you will have the opportunity to fully enjoy the relatively fast speed your connection can offer you, hence giving you an unbeatable experience when you connect online.
Reasons Why Your WiFi is So Slow
Router Location Issues
It is quite maddening when the WiFi is slow, as you will realise that it is the main cause of disruptions while watching movies or conducting online meetings. Detection of the reasons that make WiFi operate slowly will then be the first step in solving the issue and enhancing the performance of the network.
The location of the router leads to one of the most common issues with a slow WiFi connection. If the distance between the router and your device is too long or there are obstacles like walls and furniture pieces blocking the path, the signal will become weak, and as a result, the connection will be very poor. Zoning in on physical obstacles such as concrete walls, metal objects, or even large appliances can traffic the signal, causing it to lose power as it traverses these materials.
Network Congestion
Along with the choice of a network, one of the leading factors causing slow WiFi is network congestion. In households that have several devices running in the network, the bandwidth can be packed with traffic and might be inadequate to cover all the devices’ requirements if there are numerous devices in a house like cell phones, computers, smart TVs and other internet-connected devices and they are using the network at the same time. Each device competes for a piece of the internet connection, which results in the acceleration and deceleration of the internet signal for everyone. It gets worse at peak periods when family members are crowding the network by opening multiple connections.
The age and technology of your router are also determining factors in WiFi speed. Older routers that fail to meet the current wireless protocol standards and offer less functionality than their newer, more modern counterparts might be the ones that lack compatibility with networks. With the growth in technology, the requirements of home networks change accordingly. A router that has not been updated or replaced for a long time might be unable to provide the speed that is needed for current internet usage.
Interference and Security Issues
Devices operating under unprotected conditions that are not monitored and managed by the network will bring about the depression of WiFi and the decrease in data switching speeds as a result of the interference from the transmissions of neighbouring networks. Moreover, when there is too much traffic on the channels, the channels can be overlapped, thus breaking the communication signal. This could be because of an interfering WiFi network in your neighbour’s residence or on other devices found in your house, such as microwave ovens and cordless phones operating at the same frequencies.
In addition, the applications installed on the devices can also influence the network performance of the entire system. Downloading and uploading videos, watching streaming sets, online gaming, and so on are the activities that access a lot of the bandwidth, thus leaving an insufficient amount for the other users on the network.
Moreover, the security issue may further slow down the network. If the network is not protected with a good password, there might be a possibility that intruders can easily gain access to the network without the owner’s knowledge. Thus, this unauthorized intrusion may cause network congestion, and through that, we may not get the speeds, as additional devices will compete for the bandwidth.
How to Speed Up Your WiFi
WiFi network optimization starts with smart router placement. Think about the layout of your house and place the router centrally, raised above the ground and away from metal objects or thick walls. This central, unhindered location facilitates the effective reach of signals throughout more areas.
Knowing frequency ranges is essential; modern dual-band routers provide 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz choices. While 2.4 GHz offers better wall penetration and range, 5 GHz speeds adjacent devices faster. Based on their location and use, match your devices to the proper band.
Often, the cause of performance problems is channel congestion. Using network analysis tools, find less crowded channels—especially in apartment buildings where several networks fight for space. If you have many connected gadgets, think about switching to WiFi 6 technology since it manages several connections more effectively.
Using a mesh network system instead of conventional range extenders will help with ongoing connection issues. Mesh systems route devices automatically to the strongest signal, building a flawless network all around your house. For dependability and speed, nothing compares to a direct Ethernet connection for important devices like gaming systems or work computers.
Recall that performance is directly impacted by network security; an unsecured network lets unwanted users drain your bandwidth. When WPA3 encryption is available, turn it on; routinely update the firmware of your router to fix security flaws and increase performance.
Why Does My WiFi Keep Disconnecting? Final Reasons and Solutions
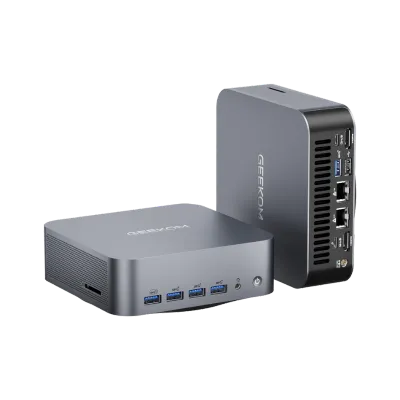
Recommendations: Dual NIC Mini PC—GEEKOM GT1 Mega

If you are interested in getting a small and powerful computer, the GEEKOM GT1 Mega might be a good choice. A great feature for users who need both wired and wireless connectivity is presented. Whether you are into casual browsing or your demands go much further, such as gaming and video editing, the Intel® Core™ Ultra 9 185H will be useful to you.
The GEEKOM GT1 Mega stands out with its dual 2.5G Ethernet ports, which deliver very stable wired connections—this will be especially beneficial in environments that require reliable internet access. With two NICs functioning simultaneously, a kind of parallel internet interface, users can connect to the network over either wire or wirelessly without having any performance implications.
Aside from its flourishing processing potency, the GEEKOM GT1 Mega now has support for WiFi 7, which comes with better speed and lower latency than the previous generations. This new uptrend in the world of wireless tech can enrich a user’s experience in streaming and online gaming.
Its design and flawlessly working cooling system makes the GEEKOM GT1 Mega an excellent choice for implementation in a home office or as part of setting up a media centre. Windows 11 Pro is pre-installed, and it’s ready for use right from the start; you won’t even need to install it if you are willing to increase your computer’s performance with sale software.
Based on the information above, the GEEKOM GT1 Mega offers the features of performance, network connectivity, and modern technology together under one roof, which might be the most suitable choice for anybody wanting to purchase a small PC.
- Intel® Core™ Ultra 9 185H.
- Intel® Arc™ Graphics supports Ray Tracing and XeSS.
- Dual-channel DDR5-5600 SODIMM, up to 64 GB.
- M.2 2280 PCIe 4.0 ×4 SSD, up to 2 TB.
- Dual 2.5G Ethernet ports, Intel® Bluetooth® 5.4 and Wi-Fi 7.
- Innovative and Efficient Cooling System – IceBlast 2.0
- Sleek, compact, scratch-resistant, and VESA-compatible.
- Pre-installed with Windows 11 Pro, ready to use.

























